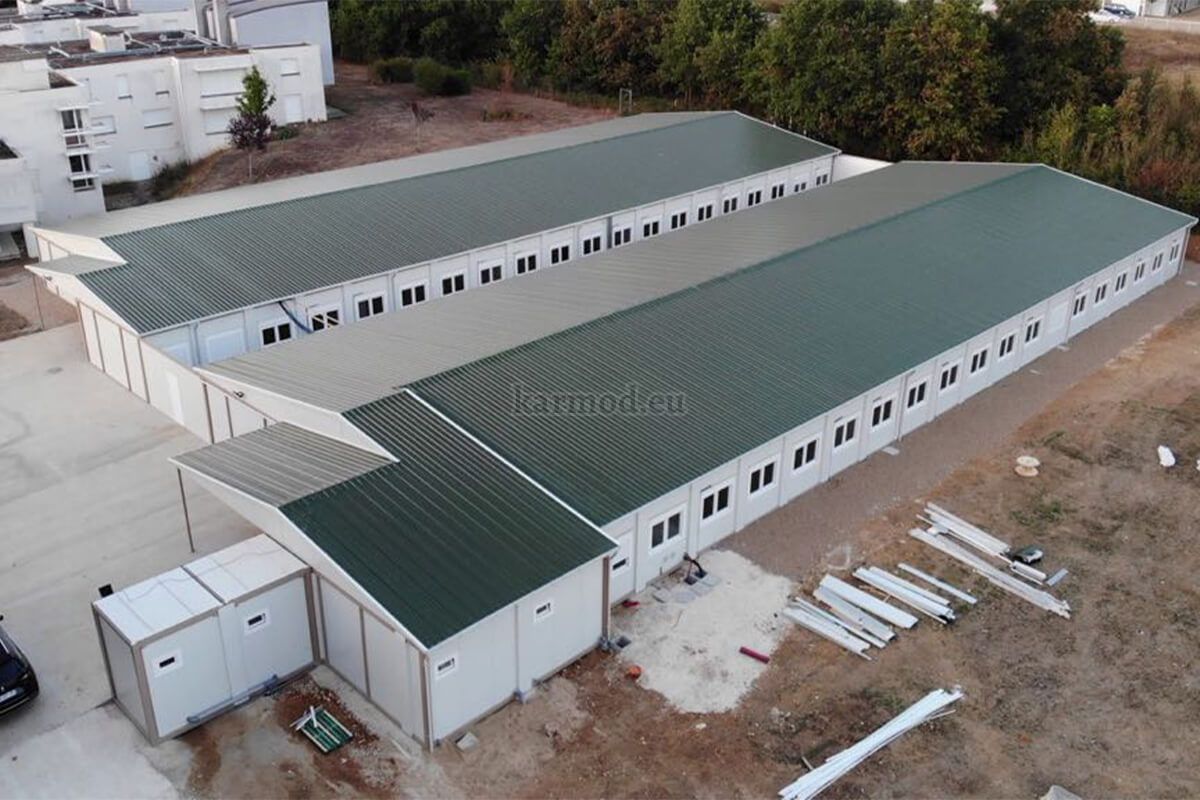
The permanent modular construction is leading the way as the construction industry changes quickly. This novel method of prefabricating modules in a factory and transporting and assembling them on-site has revolutionized the building business. It affects residential complexes, schools, and hospitals.

Time savings is a major benefit of permanent modular construction. Weather, manpower, and material shortages can delay traditional construction processes. Modular building avoids many of these issues by allowing most construction to happen off-site in a controlled environment. This concurrent site work and building manufacturing can cut project timetables, benefiting developers and investors.
Quality control is another benefit. Factory-controlled module production requires strict quality inspections and precision fabrication. Modular buildings may have greater build quality because they can attain this level of control, which is difficult on traditional construction sites. This is especially important in quality-sensitive businesses like healthcare.
Cost savings is another reason modular building is appealing. Initial costs may be comparable to typical building methods, but long-term savings are evident. Shorter building times reduce labor costs, and factories may use materials more efficiently and waste less. The faster construction time implies buildings can be operational and profitable sooner.
The method has drawbacks. Logistics are difficult, especially when moving finished modules to the construction site. This can be troublesome for huge projects or in restricted places. Industry misconceptions include that modular buildings are less durable or attractive than traditional buildings. These biases can be overcome with ongoing education and modular construction project showcases.
Modular construction also requires careful planning and design. Off-site module manufacturing limits adjustments once production begins. This demands precise early planning and coordination, which might limit flexibility in projects.
Modular building has uneven sustainability results. In the production, materials are used more efficiently and controlled, reducing waste. However, transporting modules to the site, especially over large distances, can harm the environment.
Modular buildings’ versatility and scalability are also important. They are easily extensible but have design and structural complexity restrictions. Modular construction may face engineering issues with high-rise buildings.